What Is Carotid Stenosis?
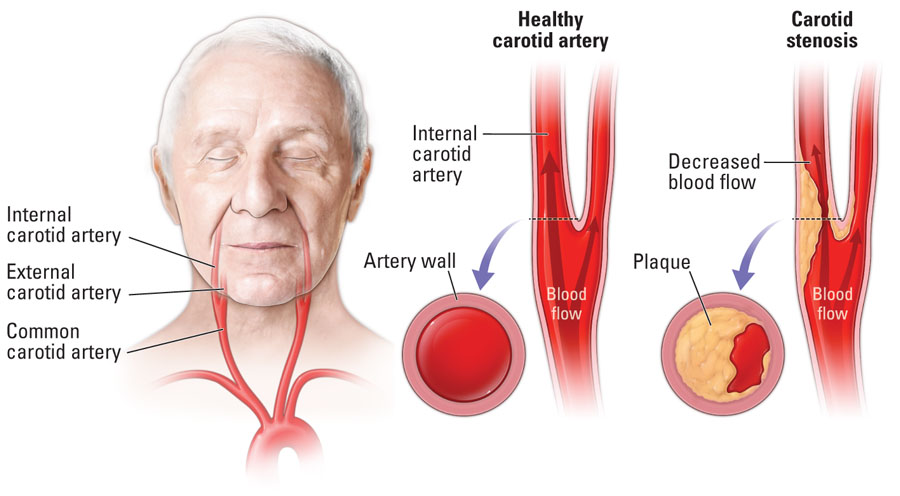
Carotid stenosis is a narrowing of the two major arteries located on either side of the neck, which carry oxygen-rich blood to the brain, head and face. It is typically a result of atherosclerosis, or plaque deposits on the arterial walls. If left untreated, carotid stenosis can lead to stroke.
While blood supplies oxygen to the body, it also contains fat, calcium and other substances that can slowly build up in the arteries, causing carotid stenosis. Some of this plaque build-up occurs naturally as we age, but certain dietary and lifestyle habits can slow down or speed up that process.
Besides age, major risk factors for carotid stenosis include:
-
Smoking
-
Inactivity
Symptoms
Doctors can sometimes detect carotid stenosis with a stethoscope, but the condition often goes undiagnosed until the symptoms become more severe. Symptoms include:
-
Dizziness, fainting and blurred vision — These symptoms can be warning signs that the brain is oxygen deprived.
-
Transient ischemic attack — A TIA, or “mini-stroke,” causes brief oxygen deprivation to the brain and temporary stroke-like symptoms, such as difficulty communicating. It is often the first sign of carotid stenosis.
-
Stroke — Stroke occurs when the blood flow to part of the brain is cut off, often leading to permanent brain damage or death.
Treatment Options
Except in severe cases, carotid stenosis can be treated with minimally invasive techniques. Treatment options include:
-
Angioplasty — A catheter with a balloon tip is run from an incision in the wrist or groin to the area of the blockage, where the balloon is inflated to widen the artery.
-
Stenting — A stent is a tiny tube used to hold an artery open after angioplasty.
-
Carotid endarterectomy — In severe cases of carotid stenosis, the patient is put under general anesthesia while the surgeon removes the blockage and any diseased parts of the artery.
Ready for an Appointment?
If you're experiencing signs or symptoms of carotid stenosis, schedule an appointment or call 800-TEMPLE-MED (800-836-7536) today.
Learn more about our doctors and care team who diagnose and treat carotid stenosis.